MLA Book Citation: A Comprehensive Guide
The Modern Language Association (MLA) style is widely used in the humanities for citing sources. Understanding how to properly cite books in MLA format is crucial for academic integrity and effective research communication. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of MLA book citations, encompassing various scenarios and offering practical examples. We will cover the core elements of an MLA book citation, along with variations for different types of books, including single-author books, edited books, books with multiple authors, and chapters within books. We will also address the crucial aspects of in-text citations to maintain consistency and clarity throughout your academic writing.
Understanding the Core Elements of an MLA Book Citation
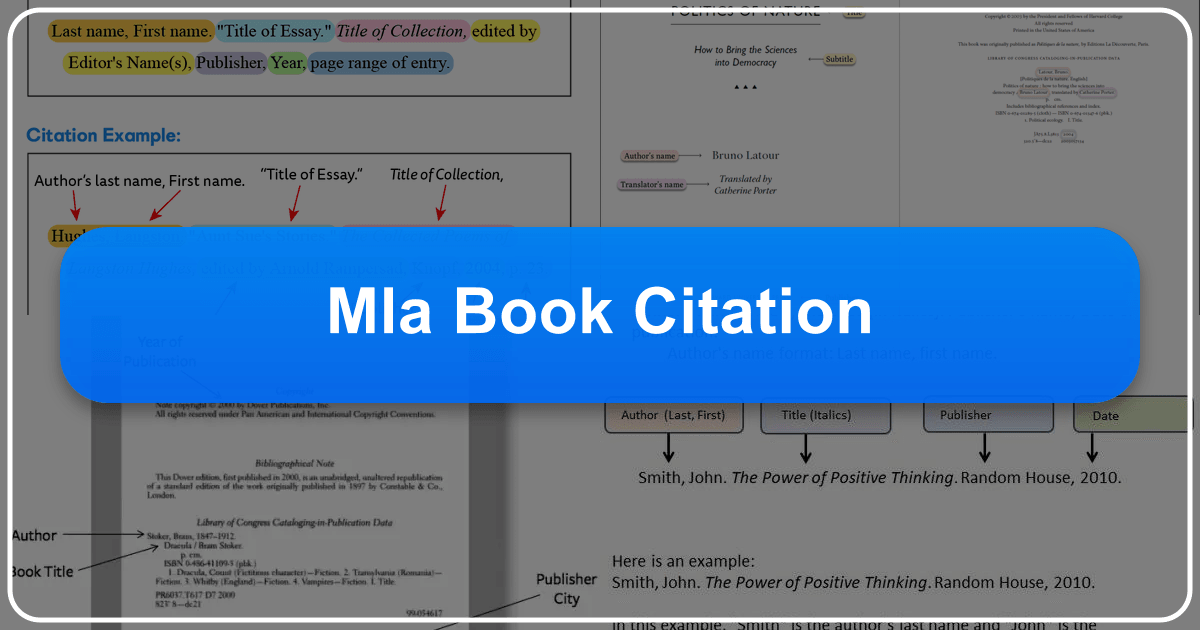
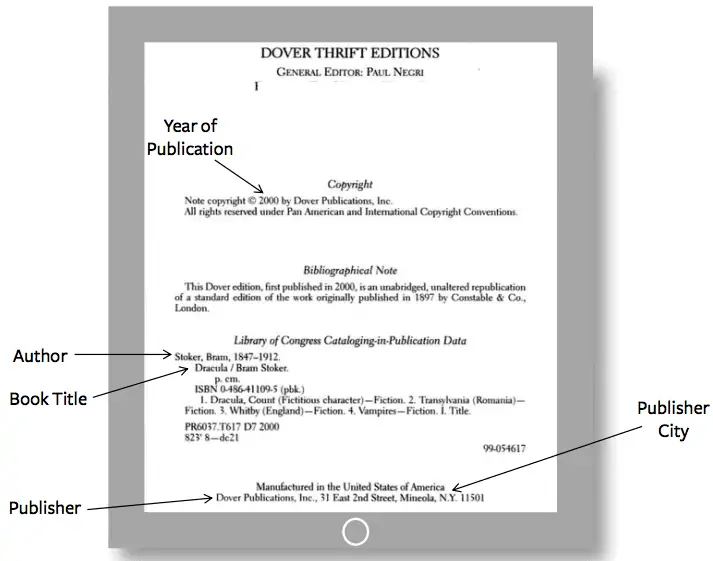
Before exploring specific examples, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental components of an MLA book citation. While the specifics may vary depending on the type of book (single author, edited volume, etc.), the core elements remain consistent and are foundational to accurate citation. These core elements, as outlined in the MLA Handbook, form the basis of every entry in your Works Cited page. These include:

- Author: The author’s name, typically presented as Last Name, First Name. If there are multiple authors, list them in the order they appear in the book. For works with three or more authors, use the first author’s name followed by “et al.”
- Title of Source: This is the title of the book. In MLA style, titles of books are italicized. Capitalize all principal words (nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, and some conjunctions).
- Title of Container (if applicable): This refers to a larger work containing the book if it’s part of a collection or series. For instance, if the book is an edition within a larger set, the series title is included here, also italicized. If the book is a standalone work (e.g., a novel), this element is omitted.
- Contributors (if applicable): If there are editors, translators, or other contributors significantly involved, their names and roles are included. For example, you might include “Edited by” followed by the editor’s name.
- Version (if applicable): This element specifies the edition (e.g., 2nd ed., 3rd ed., rev. ed.). If the book is not the first edition, clearly indicate which edition it is.
- Number (if applicable): For multi-volume works, this field indicates the volume number. For journal articles within a book, this would include the volume and issue numbers.
- Publisher: The name of the publisher responsible for the book’s publication.
- Publication Date: The year the book was published.
- Location (if applicable): This element specifies the location of the cited material within the book. For print sources, this typically includes page numbers (or a range of pages). For electronic sources, this may involve a DOI (Digital Object Identifier), a URL (Uniform Resource Locator), or a section/chapter number.
MLA Book Citation Examples: Different Scenarios
Let’s examine how these core elements come together in different citation scenarios:
1. Books with One Author
This is the most straightforward scenario. The citation includes the author’s name (last name first), the book title (italicized), the publisher, and the publication year.
Example:
Austen, Jane. Pride and Prejudice. Penguin Classics, 2003.
2. Books with Two or More Authors
For books with two authors, list both names in the order they appear on the book’s title page. For books with three or more authors, use the first author’s last name followed by “et al.”
Example (Two Authors):

Smith, John, and Jane Doe. The History of X. Oxford University Press, 2010.
Example (Three or More Authors):
Jones, Robert, et al. Advanced Physics. Cambridge University Press, 2015.
3. Edited Books
When citing an edited book, the editor’s name replaces the author’s name, followed by “editor” (or “editors” if there are multiple).
Example:
Shakespeare, William. Hamlet. Edited by Harold Bloom. Bloomsbury, 2005.
4. Books with a Translator
If the book has been translated, include the translator’s name after the title, preceded by “Translated by.”
Example:
Cervantes, Miguel de. Don Quixote. Translated by Edith Grossman. Harper Perennial Modern Classics, 2003.
5. Chapters or Essays in Edited Books
When citing a specific chapter or essay within an edited book, the format is similar to the single-author book, but with added information specifying the chapter and the edited collection.
Example:
Smith, Alice. “The Impact of Technology.” The Digital Age, edited by Bob Johnson, McGraw-Hill, 2020, pp. 150-175.
6. eBooks and Digital Books
Citing eBooks follows a similar structure to print books, but with the addition of information identifying the ebook edition and its access location (e.g., platform or URL).
Example:
Carroll, Lewis. Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland. eBook ed., Project Gutenberg, 2008, www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/11.
In-Text Citations in MLA Style
In-text citations are brief references within the main body of your paper that correspond to the full citations in your Works Cited page. They usually include the author’s last name and the page number(s) where the information is found. For example, if you were quoting from Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice, you might include a parenthetical citation like this: (Austen 120). If there is no page number (e.g., for a website or eBook), use the author’s last name only.
Example (with page number):
“It is a truth universally acknowledged, that a single man in possession of a good fortune, must be in want of a wife.” (Austen 1).
Example (without page number):
According to Smith’s analysis, the impact is significant (Smith).
The Importance of Accuracy and Consistency
Accurate and consistent citation is paramount in academic work. Inaccuracies can be perceived as plagiarism or a lack of scholarly rigor. Always double-check the source material for complete and accurate information. Consistent application of MLA style throughout your paper demonstrates attention to detail and strengthens the credibility of your work. Remember to consult the most current edition of the MLA Handbook for the most up-to-date guidelines. Numerous online resources and guides, including those from Lbibinders.org, can provide further assistance in mastering MLA citation. By following these guidelines and utilizing available resources, you can confidently and accurately cite books in your academic writing.